Village in Illinois, United States
Show map of the United States
|
Hoffman Estates, Illinois
|

Hoffman Estates scenery
|

Flag

Seal
|
| Motto:
"Growing to Greatness"
|
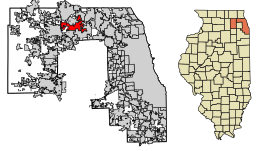
Location of Hoffman Estates in Cook County, Illinois
|
Show map of Chicago metropolitan area
|
Coordinates:
42°03′50″N 88°08′49″W / 42.06389°N 88.14694°W / 42.06389; -88.14694CountryUnited StatesStateIllinoisCountiesCookTownshipsSchaumburg, Palatine, Hanover, BarringtonIncorporated1959 (village)Government
• MayorWilliam D. McLeod[citation needed] • Village ManagerEric J. Palm[citation needed]Area
[1]
• Total
21.25 sq mi (55.03 km2) • Land21.07 sq mi (54.56 km2) • Water0.18 sq mi (0.47 km2) 0.86%Elevation
[2]
824 ft (251 m)Population
(2020)
• Total
52,530 • Density2,493.71/sq mi (962.82/km2)Zip Code
60169, 60010, 60192
Area code(s)847 / 224FIPS code17-35411GNIS feature ID2398519[2]Websitewww.hoffmanestates.org
Hoffman Estates is a village in Cook County, Illinois, United States. It is a suburb of Chicago. Per the 2020 census, the population was 52,530.[3]
The village previously served as the headquarters for Sears and is one of the American headquarters for Mori Seiki. Now Arena, home of the Windy City Bulls of the NBA G League is part of the village. Between 2006 and 2009, the village hosted the Heartland International Tattoo, one of the largest music and dance festivals of its kind in the Midwest.
History
[edit]
 Sunderlage Farm Smokehouse[4](National Register of Historic Places) in Hoffman Estates
Sunderlage Farm Smokehouse[4](National Register of Historic Places) in Hoffman Estates
Prior to the 1940s, German settlers moved into the area west of Roselle Road and north of Golf Road, then known as Wildcat Grove. The area was sparsely populated until farmers purchased land in the area in the 1940s.
In 1954, Sam and Jack Hoffman, owners of a father-son owned construction company, bought 160 acres of land in the area.[5] The pair constructed homes and began the development of the region which now bears their name. As residents moved in, they voted to incorporate the area, and the Village of Hoffman Estates was incorporated on September 23, 1959.[6][5][7] In 1973, six former town officials, including mayors Edward F. Pinger (1959−1965) and Roy L. Jenkins (1965−1969) were indicted on bribery and tax charges.[8]
Once the Northwest Tollway opened, Schaumburg Township became more attractive to Chicago commuters. In the early 1960s, land annexations north of the tollway and in other neighboring regions more than doubled Hoffman Estates' land area.[9]
The opening of the Woodfield Mall in Schaumburg to the east in 1971 made the area a major business center. An attempt to change the name of the village to East Barrington, among other names, was made in the early 1980s but failed upon a residential vote.[10]
In the 1990s, the Prairie Stone Business Park began development. This 750-acre (3.0 km2) planned multi-purpose business park[11] is bounded by Illinois Route 59 on the east, Interstate 90 on the south, Illinois Route 72 on the north, and Beverly Road on the west. The business park came to fruition in 1993 when Sears, Roebuck and Company relocated from the Sears Tower in Chicago to a sprawling headquarters in the northwest part of Prairie Stone.[12][11] That was followed in by Indramat and Quest International, which in 1995 also opened facilities in the park.[13][14][15] Throughout the 1990s, a health and wellness center and child care facility were developed, as well as other smaller office buildings, and a branch of Northern Illinois University. Development of the business park is still ongoing, and recent additions in the 2000s include the 11,000-seat Now Arena; office buildings for Serta, WT Engineering, I-CAR, and Mary Kay; a Cabela's outdoor outfitters store; a 295-room Marriott hotel; and the 400,000-square-foot (37,000 m2) Poplar Creek Crossing Retail Center, which is anchored by Target and numerous other big-box retailers. Future development will include further office buildings and retail development, Sun Island Hotel and Water Park, an amphitheater, and restaurants.
In 2011, the Village of Hoffman Estates took over ownership of the Now Arena.[16] On June 23, 2020, the Village of Hoffman Estates approved an $11.5 million deal to rename the Sears Centre Arena to the "NOW Arena".[17]
In the fall of 2016, papers and artifacts from President Barack Obama's administration began to arrive in town, where they are being stored in a building on Golf Road. The site is their temporary home while construction takes place on the Barack Obama Presidential Center in Jackson Park, Chicago, and is not open to the public.[18]
In January 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed the second U.S. case of COVID-19 in a Hoffman Estates resident. The patient, a woman in her 60s returning from Wuhan, China, was treated at St. Alexius Medical Center.[19] Her husband was later infected in the first case of human-to-human transmission of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the United States.[20]
Geography
[edit]
According to the 2021 census gazetteer files, Hoffman Estates has a total area of 21.25 square miles (55.04 km2), of which 21.07 square miles (54.57 km2) (or 99.15%) is land and 0.18 square miles (0.47 km2) (or 0.85%) is water.[21]
Demographics
[edit]
Historical population
| Census |
Pop. |
Note |
%± |
| 1960 |
8,296 |
|
— |
| 1970 |
22,238 |
|
168.1% |
| 1980 |
37,272 |
|
67.6% |
| 1990 |
46,363 |
|
24.4% |
| 2000 |
49,495 |
|
6.8% |
| 2010 |
51,895 |
|
4.8% |
| 2020 |
52,530 |
|
1.2% |
Hoffman Estates village, Illinois – Racial and ethnic composition
Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate category. Hispanics/Latinos may be of any race.
| Race / Ethnicity (NH = Non-Hispanic) |
Pop 2000[25] |
Pop 2010[23] |
Pop 2020[24] |
% 2000 |
% 2010 |
% 2020 |
| White alone (NH) |
33,789 |
29,357 |
26,014 |
68.27% |
56.57% |
49.52% |
| Black or African American alone (NH) |
2,141 |
2,393 |
2,472 |
4.33% |
4.61% |
4.71% |
| Native American or Alaska Native alone (NH) |
54 |
60 |
69 |
0.11% |
0.12% |
0.13% |
| Asian alone (NH) |
7,429 |
11,701 |
13,733 |
15.01% |
22.55% |
26.14% |
| Pacific Islander alone (NH) |
10 |
4 |
2 |
0.02% |
0.01% |
0.00% |
| Other race alone (NH) |
73 |
70 |
183 |
0.15% |
0.13% |
0.35% |
| Mixed race or Multiracial (NH) |
801 |
1,013 |
1,579 |
1.62% |
1.95% |
3.01% |
| Hispanic or Latino (any race) |
5,198 |
7,297 |
8,478 |
10.50% |
14.06% |
16.14% |
| Total |
49,495 |
51,895 |
52,350 |
100.00% |
100.00% |
100.00% |
As of the 2020 census[26] there were 52,530 people, 18,110 households, and 14,048 families residing in the village. The population density was 2,472.58 inhabitants per square mile (954.67/km2). There were 19,160 housing units at an average density of 901.86 per square mile (348.21/km2). The racial makeup of the village was 52.08% White, 26.26% Asian, 4.87% African American, 0.60% Native American, 0.02% Pacific Islander, 7.51% from other races, and 8.68% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 16.14% of the population.
There were 18,110 households, out of which 36.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.71% were married couples living together, 11.97% had a female householder with no husband present, and 22.43% were non-families. 18.07% of all households were made up of individuals, and 5.43% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 3.16 and the average family size was 2.77.
The village's age distribution consisted of 23.1% under the age of 18, 7.3% from 18 to 24, 27.7% from 25 to 44, 28.3% from 45 to 64, and 13.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38.2 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.6 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.4 males.
The median income for a household in the village was $92,423, and the median income for a family was $103,641. Males had a median income of $56,210 versus $42,288 for females. The per capita income for the village was $40,016. About 3.3% of families and 4.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 4.9% of those under age 18 and 3.5% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
[edit]
Employers
[edit]
Many Japanese companies have their U.S. headquarters in Hoffman Estates and Schaumburg[27] but the largest employers in Hoffman Estates as of 2023[28] are:
| No. |
Employer |
No. of employees |
| 1 |
St. Alexius Medical Center |
2,500 |
| 2 |
Siemens Medical Systems |
400 |
| 3 |
Claire's[29] |
400 |
| 4 |
Village of Hoffman Estates |
370 |
| 5 |
FANUC America[30] |
350 |
| 6 |
Vistex |
350 |
| 7 |
Leopardo Companies, Inc. |
300 |
| 8 |
Wells Fargo |
300 |
| 9 |
The Salvation Army |
270 |
| 10 |
Tate & Lyle |
220 |
Education
[edit]
The village is served by several public school districts. The majority of residents who live in Schaumburg Township attend:
- Township High School District 211 (9–12)[31]
- Community Consolidated School District 54 (K–8)[32]
North Hoffman Estates (north of I-90) residents are served by:
- Township High School District 211
- Community Consolidated School District 15 (K–8)[33] (East of Huntington Blvd)
- Barrington School District 220 (K–12) (Unit District) (West of Huntington Blvd).[34]
Residents west of Barrington Road primarily attend Unit School District, Elgin Area U46.
High schools
[edit]
Schools located in the Hoffman Estates village limits:
- Hoffman Estates High School
- James B. Conant High School
Other high schools in the same township high school district:
- Schaumburg High School
- William Fremd High School
- Palatine High School
[edit]
Most of the village is served by Harper College Community College District 512.
Miscellaneous education
[edit]
The Xilin Northwest Chinese School (simplified Chinese: 希æžâ€â€ÃƒÂ¨Ã‚¥Â¿Ã¥Å’â€â€ÃƒÂ¤Ã‚¸ÂÂæ–‡å¦校; traditional Chinese: 希æžâ€â€ÃƒÂ¨Ã‚¥Â¿Ã¥Å’â€â€ÃƒÂ¤Ã‚¸ÂÂæ–‡å¸校; pinyin: XÄ«lín XÄ«bÄ›i ZhÃ…ÂÂngwén Xuéxiào) holds its classes at Conant High School in Hoffman Estates.[35] It serves grades preschool through 12.[36] The school predominately serves mainland Chinese families. In 2003 the school held its classes in Palatine High School in Palatine. In 2000 the school had served around 300 students. This figure increased almost by 100%, to almost 600 students. This made it one of the largest of the Chinese schools in the Chicago area.[37]
Library
[edit]
 Chicago portal
Chicago portal Illinois portal
Illinois portal
- Barrington Area Library
- Schaumburg Township District Library
- Gail Borden Public Library District
- Palatine Township Library
Sister city
[edit]
Hoffman Estates has one sister city:[38]
- Angoulême, Charente, Nouvelle-Aquitaine, France
Transportation
[edit]
Pace provides bus service on multiple routes connecting Hoffman Estates to Elgin, Rosemont, and other destinations.[39]
Notable people
[edit]
- Tammy Duckworth, U.S. Senator from Illinois (2016–present)[40]
- Rob Valentino (b. 1985), former soccer player who is an assistant coach for Atlanta United[41]
- William Beckett, lead singer of the band The Academy Is...
Notes
[edit]
- ^
"2020 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 15, 2022.
- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Hoffman Estates, Illinois
- ^ "Hoffman Estates village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 15, 2022.
- ^ "The Sunderlage Smokehouse: Hoffman Eestates' National Register Landmark". History of Schaumburg Township: A Blog of the Schaumburg Township District Library. February 21, 2010. Retrieved March 3, 2017.
- ^ a b Collins, Catherine (August 24, 1986). "Hoffman Estates Plans a Revamp of Future Image". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ "Hoffman Estates, IL". The Encyclopedia of Chicago. Retrieved March 8, 2020.
- ^ "HR0614 96th General Assembly". State of Illinois.
- ^ Davis, Robert (October 27, 1973). "U.S. indicts builder, seven ex-officials in suburb bribe". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ "History of Hoffman Estates". Village of Hoffman Estates. Retrieved March 8, 2020.
- ^ "Name history of Hoffman Estates". Falcon Living. Retrieved November 26, 2017.
- ^ a b Sulski, Jim (May 11, 2000). "Versatile Network Brings Workers to Prairie Stone Business Park". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ Bernstein, David (May 16, 2020). "The Sears Headquarters Deal Cost Taxpayers $500 Million. 30 Years Later, There's Little to Show for It". ProPublica.
- ^ Russis, Martha (December 28, 1994). "PRAIRIE STONE GETS ELECTRONIC FIRM FOR TENANT". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ Kerch, Steve (October 30, 1994). "GETTING THE NOD". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ "Village of Hoffman Estates: History of Hoffman Estates". Hoffmanestates.com. Archived from the original on May 11, 2012. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ Manson, Ken (December 23, 2009). "Suburb takes over Sears Centre". Chicago Tribune.
- ^ Zumbach, Lauren (June 23, 2020). "Sears name disappearing from another Chicago-area building. Hoffman Estates arena gets a new name this fall". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved June 24, 2020.
- ^ Skiba, Katherine (October 21, 2016). "Military Soon to Start Moving Obama's Papers to Hoffman Estates". Chicago Tribune. Washington DC. Retrieved March 3, 2017.
- ^ "Coronavirus Confirmed In Chicago; Woman In Her 60s Being Treated For Symptoms". CBS Chicago. Chicago. January 24, 2020. Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ Hauck, Grace (January 30, 2020). "Chicago man is first US case of person-to-person coronavirus spread". USA Today. Chicago. Retrieved February 13, 2020.
- ^ "Gazetteer Files". Census.gov. Retrieved June 29, 2022.
- ^ "Decennial Census of Population and Housing by Decades". US Census Bureau.
- ^ a b "P2 Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2010: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – Hoffman Estates village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ a b "P2 Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) –Hoffman Estates village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "P004: Hispanic or Latino, and Not Hispanic or Latino by Race – 2000: DEC Summary File 1 – Hoffman Estates village, Illinois". United States Census Bureau.
- ^ "Explore Census Data". data.census.gov. Retrieved June 28, 2022.
- ^ Selvam, Ashok. "Asian population booming in suburbs". Daily Herald (Arlington Heights, Illinois). March 6, 2011. Retrieved on June 19, 2013.
- ^ "Village of Hoffman Estates Comprehensive Annual Financial Report". June 25, 2024.
- ^ " FAQ Archived July 13, 2014, at the Wayback Machine." Claire's. Retrieved on December 25, 2011. "Claire’s Stores, Inc. has its investor relations and customer service located in Pembroke Pines , Florida . The buying, marketing and distribution offices are located in Hoffman Estates, a suburb of Chicago . Please visit Contact Us if you would like to send correspondence to our corporate headquarters."
- ^ "Village of Hoffman Estates Top Employers". Hoffmanestates.org. March 21, 2012. Archived from the original on April 22, 2012. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ "d211.org". d211.org. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ "sd54.k12.il.us". sd54.k12.il.us. April 19, 2012. Archived from the original on February 1, 1998. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ "ccsd15.net". ccsd15.net. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ "cusd220.lake.k12.il.us". cusd220.lake.k12.il.us. Archived from the original on July 3, 2006. Retrieved April 30, 2012.
- ^ "School Location." Northwest Xilin Chinese School. Retrieved on February 24, 2014. "School Address 700 East Cougar Trail,Hoffman Estates,IL 60194 Located at Conant High School campus."
- ^ "About Us." Northwest Xilin Chinese School. Retrieved on February 24, 2014.
- ^ Ray, Tiffany. "Schools connect students to China." Chicago Tribune. March 2, 2003. Retrieved on February 24, 2014.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on April 5, 2017. Retrieved April 4, 2017.
cite web: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "RTA System Map" (PDF). Retrieved January 30, 2024.
- ^ "Endorsement: Duckworth for U.S. Senate". Daily Herald. October 8, 2022.
- ^ "Rob Valentino Biography". ESPN. Retrieved March 31, 2024.
External links
[edit]
- Village of Hoffman Estates official website
Hoffman Estates, Illinois
| |
|
Education
|
| Schools |
- Community Consolidated School District 54
- Community Consolidated School District 15
- Barrington School District 220
- Township High School District 211
- Hoffman Estates High School
- James B. Conant High School
- Elgin Area School District U46
|
| Other education |
- Harper College (in Palatine)
- Schaumburg Township District Library
- Barrington Area Library
|
|
Other
|
| Landmarks |
- Now Arena
- Sunderlage Farm Smokehouse
|
|
This list is incomplete.
|
Municipalities and communities of Cook County, Illinois, United States
| |
|
County seat: Chicago
|
| Cities |
- Berwyn
- Blue Island
- Burbank
- Calumet City
- Chicago‡
- Chicago Heights
- Country Club Hills
- Countryside
- Des Plaines
- Elgin‡
- Elmhurst‡
- Evanston
- Harvey
- Hickory Hills
- Hometown
- Markham
- Northlake
- Oak Forest
- Palos Heights
- Palos Hills
- Park Ridge
- Prospect Heights
- Rolling Meadows
|
 Map of Illinois highlighting Cook County
Map of Illinois highlighting Cook County
|
| Towns |
|
| Villages |
|
| Townships |
- Barrington
- Berwyn
- Bloom
- Bremen
- Calumet
- Cicero
- Elk Grove
- Hanover
- Lemont
- Leyden
- Lyons
- Maine
- New Trier
- Niles
- Northfield
- Norwood Park
- Oak Park
- Orland
- Palatine
- Palos
- Proviso
- Rich
- River Forest
- Riverside
- Schaumburg
- Stickney
- Thornton
- Wheeling
- Worth
Former: Evanston • Hyde Park • Jefferson • Lake • Lake View • North Chicago • Rogers Park • South Chicago • West Chicago
|
Unincorporated
communities |
- Central Stickney
- Hines
- Indian Hill
- La Grange Highlands
- Nottingham Park
- Sag Bridge
- Sutton
|
| Other Communities |
|
| Footnotes |
‡This populated place also has portions in an adjacent county or counties
|
- Illinois portal
- United States portal
|
Chicago metropolitan area
| |
| Major city |
|
|
Cities
(over 30,000 in 2020) |
- Aurora
- Berwyn
- Calumet City
- Crown Point
- Crystal Lake
- DeKalb
- Des Plaines
- Elgin
- Elmhurst
- Evanston
- Gary
- Hammond
- Highland Park
- Joliet
- Kenosha
- Naperville
- North Chicago
- Park Ridge
- Portage
- St. Charles
- Valparaiso
- Waukegan
- Wheaton
|
Towns and villages
(over 30,000 in 2020) |
- Addison
- Arlington Heights
- Bartlett
- Bolingbrook
- Buffalo Grove
- Carol Stream
- Carpentersville
- Cicero
- Downers Grove
- Elk Grove Village
- Glendale Heights
- Glenview
- Grayslake
- Gurnee
- Hanover Park
- Hoffman Estates
- Lombard
- Merrillville
- Mount Prospect
- Mundelein
- Niles
- Northbrook
- Oak Lawn
- Oak Park
- Orland Park
- Oswego
- Palatine
- Plainfield
- Romeoville
- Schaumburg
- Skokie
- Streamwood
- Tinley Park
- Wheeling
- Wonder Lake
- Woodridge
|
| Counties |
- Cook
- DeKalb
- DuPage
- Grundy
- Jasper
- Kane
- Kankakee
- Kendall
- Kenosha
- Lake, IL
- Lake, IN
- McHenry
- Newton
- Porter
- Will
|
| Regions |
- Great Lakes
- Northern Illinois
- Northern Indiana
|
| Sub-regions |
- Chicago Southland
- Eastern Ridges and Lowlands
- Fox Valley (Illinois)
- Golden Corridor
- Illinois Technology and Research Corridor
- North Shore (Chicago)
- Northwest Indiana
|
|
Illinois, United States
|
Authority control databases  |
| International |
|
| National |
- Germany
- United States
- Israel
|
| Geographic |
|